Hydrogenated Bisphenol A (H-BPA)
Business segment & products
Hydrogenated Bisphenol A (H-BPA)
Our H-BPA is a dialchol with a cycloalyphatic structure, obtained by dehydrogenating bisphenol A. It is used as a raw material for various engineering plastics and paints, with its good chemical stability derived from no unsaturated bond in the structure.
| ▼ Molecular Formula | ▼ ENCS No. | ▼ Structural Formula |
|---|---|---|
| C15H28O2C | 4-201 |
2,2'-bis-(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)propane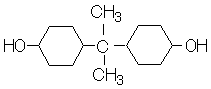 |
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| ▼ TEST | ▼ UNIT | ▼ ANALYSIS |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point (2.67kPa) | ℃ | 253.5~257 |
| Molten Viscosity (160℃) | m2/s | 17×10-6 |
| Heating Value | kJ/g | 37.21 |
| Flash Point | ℃ | 194 MIN. |
SPECIFICATIONS AND TYPICAL ANALYSIS
| ▼ TEST | ▼ UNIT | ▼ SPECIFICATIONS | ▼ TYPICAL ANALYSIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water(During manufacturing※) | % | 0.5 MAX. | 0.05 |
| Appearance | white flakes | white flakes | |
| Color(30%methanol solution) | Hazen Unit | 30 MAX. | 5 |
| Ash | ppm | 50 MAX. | 30 MAX. |
| Fe | ppm | 5 MAX. | 1 MAX. |
| Hydroxyl Group Value | mgKOH/g | 430 MIN. | 461 |
MAJOR USE: Raw Material for resins, such as epoxy, unsaturated polyester, polycarbonate, polyurethane, polyacrylate, polysulphone, alkyd.
Note
The descriptions herein are based on the available sources and information but no guarantee is given for its integrity or accuracy.

